-
1 электрический трансформатор
Русско-английский исловарь по машиностроению и автоматизации производства > электрический трансформатор
-
2 электрический трансформатор
Русско-английский научно-технический словарь Масловского > электрический трансформатор
-
3 электрический трансформатор
1) Automation: electric transformer2) Makarov: compensatorУниверсальный русско-английский словарь > электрический трансформатор
-
4 электрическая машина
электрическая машина
-
[IEV number 151-13-39]EN
electric machine
energy transducer that can transform electric energy into mechanical energy or vice versa
NOTE – The term "electric machine" is also used for synchronous compensators and torque motors.
[IEV number 151-13-39]FR
machine électrique, f
transducteur d'énergie qui peut transformer de l'énergie électrique en énergie mécanique ou inversement
NOTE – Le terme "machine électrique" est aussi employé pour les compensateurs synchrones et les machines-couples.
[IEV number 151-13-39]EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электрическая машина
-
5 комплектная трансформаторная подстанция блочная
Electric machinery: modular integrated transformer substation (КТПБ)Универсальный русско-английский словарь > комплектная трансформаторная подстанция блочная
-
6 ваттметр
electric power meter, power meter, watt-hour meter, wattmeter* * *ваттме́тр м.
wattmeterвключа́ть ваттме́тр че́рез измери́тельный трансформа́тор — connect a wattmeter (to the circuit) with the interposition of an instrument transformerрасширя́ть преде́л ваттме́тра — extend the range of a wattmeterэкрани́ровать ваттме́тр от вне́шних поле́й — shield a wattmeter from external fieldsастати́ческий ваттме́тр — astatic wattmeterболометри́ческий ваттме́тр — balometric power meterвозду́шный ваттме́тр — air-flow wattmeterваттме́тр для СВЧ — microwave wattmeter, microwave power meterзерка́льный ваттме́тр — reflecting wattmeterинтегри́рующий ваттме́тр — integrating wattmeterколориметри́ческий ваттме́тр — calorimetric power meterмногофа́зный ваттме́тр — polyphase wattmeterпереносно́й ваттме́тр — portable wattmeterваттме́тр поглоща́емой мо́щности — terminoting power meterпондеромото́рный ваттме́тр — radiation-pressure power meterваттме́тр проходя́щей мо́щности — feed-through power meterреакти́вный ваттме́тр — idle-current wattmeterсамопи́шущий ваттме́тр — recording wattmeterваттме́тр с компенси́рующей кату́шкой — composite-coil wattmeterтеплово́й ваттме́тр — thermal wattmeterферродинами́ческий ваттме́тр — ferrodynamic wattmeterщитово́й ваттме́тр — switchboard wattmeterэлектродинами́ческий ваттме́тр — dynamometer wattmeterэлектро́нный ваттме́тр — electronic power meterэлектростати́ческий ваттме́тр — electrostatic wattmeter -
7 трансформаторный усилитель
[lang name="Russian"]усилитель следящей системы; сервоусилитель — servo amplifier
Русско-английский научный словарь > трансформаторный усилитель
-
8 трансформаторная сталь
Русско-английский новый политехнический словарь > трансформаторная сталь
-
9 трансформатор
трансформатор
Статическое электромагнитное устройство, имеющее две или более индуктивно связанных обмоток и предназначенное для преобразования посредством электромагнитной индукции одной или нескольких систем переменного тока в одну или несколько других систем переменного тока
[ ГОСТ 16110-82]
трансформатор
Преобразователь электрической энергии переменного тока, который передает электрическую энергию без изменения частоты
[ОСТ 45.55-99]
трансформатор
Устройство для преобразования какого-либо существенного свойства энергии или объекта, например, переменного тока одного напряжения в переменный ток другого напряжения
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
transformer
electric energy converter without moving parts that changes voltages and currents associated with electric energy without change of frequency
[IEV number 151-13-42]FR
transformateur, m
convertisseur d'énergie électrique sans pièces mobiles qui modifie les tensions et courants associés à une énergie électrique sans changement de fréquence
[IEV number 151-13-42]Принцип действия трансформатора
Трансформатором называется аппарат, преобразующий переменный ток одного напряжения в переменный ток другого напряжения, но той же частоты.
Устройство трансформатора следующее. На сердечник из мягкой стали намотаны две обмотки. Обмотка, к которой подводится напряжение, называется первичной. Ток, проходя по первичной. обмотке, создает магнитное поле, индукционные линии которого замыкаются по сердечнику. Обмотка, в которой будет наводиться э. д. с., используемая далее во внешней цепи, называется вторичной обмоткой.
Если первичную обмотку трансформатора питать переменным током, т. е. током, изменяющимся с определенной частотой по величине направлению, то в замкнутой вторичной обмотке также будет протекать переменный ток и включенные в нее электрические лампы будут гореть ровно, не мигая. Отсюда видно, что работа трансформатора основана на использовании явления взаимоиндукции.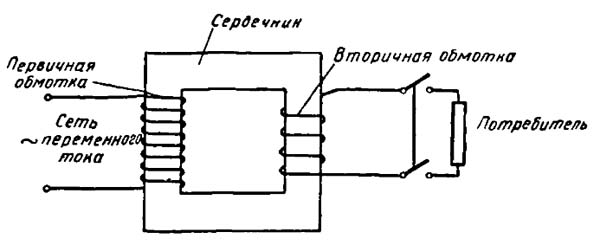
Схема устройства трансформатора
[Кузнецов М. И. Основы электротехники. М, "Высшая Школа", 1964]
Тематики
Классификация
>>>EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > трансформатор
-
10 фазовый угол
фазовый угол
угол сдвига фаз
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
If the phase currents are connected correctly and there is an ideal balanced load on the transformer, the phase angles between the phase currents of any one transformer end are displayed as follows:
[Schneider Electric]При правильном подключении фазных проводов и идеально симметричной нагрузке трансформатора фазовые углы между фазными токами рассматриваемой стороны трансформатора должны отображаться следующим образом:
[Перевод Интент]The phase angle between the phase currents of two transformer ends for a particular phase is a function of the vector group of the transformer.
[Schneider Electric]Фазовый угол между фазными токами двух сторон трансформатора относительно определенной фазы является функцией группы соединений обмоток трансформатора.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > фазовый угол
-
11 Ilgner, Karl
SUBJECT AREA: Electricity[br]b. 27 July 1862 Neisse, Upper Silesia (now Nysa, Poland)d. 18 January 1921 Berthelsdorf, Silesia[br]German electrical engineer, inventor of a transformer for electromotors.[br]Ilgner graduated from the Gewerbeakademie (the forerunner of the Technical University) in Berlin. As the representative of an electric manufacturing company in Breslau (now Wroclaw, Poland) from 1897, he was confronted with the fact that there were no appropriate drives for hoisting-engines or rolling-plants in steelworks. Two problems prevented the use of high-capacity electric motors in the mining as well as in the iron and steel industry: the reactions of the motors on the circuit at the peak point of stress concentration; and the complicated handling of the control system which raised the risks regarding safety. Having previously been head of the department of electrical power transmission in Hannover, he was concerned with the development of low-speed direct-current motors powered by gas engines.It was Harry Ward Leonard's switchgear for direct-current motors (USA, 1891) that permitted sudden and exact changes in the speed and direction of rotation without causing power loss, as demonstrated in the driving of a rolling sidewalk at the Paris World Fair of 1900. Ilgner connected this switchgear to a large and heavy flywheel which accumulated the kinetic energy from the circuit in order to compensate shock loads. With this combination, electric motors did not need special circuits, which were still weak, because they were working continuously and were regulated individually, so that they could be used for driving hoisting-engines in mines, rolling-plants in steelworks or machinery for producing tools and paper. Ilgner thus made a notable advance in the general progress of electrification.His transformer for hoisting-engines was patented in 1901 and was commercially used inter alia by Siemens \& Halske of Berlin. Their first electrical hoisting-engine for the Zollern II/IV mine in Dortmund gained international reputation at the Düsseldorf exhibition of 1902, and is still preserved in situ in the original machine hall of the mine, which is now a national monument in Germany. Ilgner thereafter worked with several companies to pursue his conception, became a consulting engineer in Vienna and Breslau and had a government post after the First World War in Brussels and Berlin until he retired for health reasons in 1919.[br]Bibliography1901, DRP no. 138, 387 1903, "Der elektrische Antrieb von Reversier-Walzenstraßen", Stahl und Eisen 23:769– 71.Further ReadingW.Kroker, "Karl Ilgner", Neue Deutsche Biographie, Vol. X, pp. 134–5. W.Philippi, 1924, Elektrizität im Bergbau, Leipzig (a general account).K.Warmbold, 1925, "Der Ilgner-Umformer in Förderanlagen", Kohle und Erz 22:1031–36 (a detailed description).WK -
12 виртуальная обмотка трансформатора
виртуальная обмотка трансформатора
виртуальная сторона трансформатора
-
[Интент]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
The virtual end is formed by adding the corresponding currents of two transformer ends.
[Schneider Electric]Виртуальная обмотка трансформатора образуется путем суммирования соответствующих токов двух обмоток трансформатора.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > виртуальная обмотка трансформатора
-
13 преобразователь
conversion device, converter, changer, inverter, transducer, transformer, translator* * *преобразова́тель м.
converterпреобразова́тель ана́лог — код — analog-to-number converterана́лого-цифрово́й преобразова́тель — analog-to-digital [A/ D] converter, digitizerпреобразова́тель вал — код — shaft position encoder, shaft digitizerпреобразова́тель ви́да колеба́ний — mode transducer, mode transformerвре́мя-и́мпульсный преобразова́тель — time-to-pulse converterпреобразова́тель да́нных — ( в системе передачи данных) data set; ( в двусторонних системах) modemизмери́тельный преобразова́тель ( прежнее наименование прибо́рный да́тчик) — (instrument) transducerизмери́тельный, биоэлектри́ческий преобразова́тель — bioelectric transducerизмери́тельный преобразова́тель давле́ния — pressure transducerизмери́тельный преобразова́тель механи́ческой величины́ в электри́ческую — mechanical-to-electric transducerизмери́тельный, силово́й преобразова́тель — force transducerизмери́тельный, тензометри́ческий преобразова́тель — strain transducerпреобразова́тель изображе́ний — image converterпреобразова́тель ко́да — code converter, code translatorпреобразова́тель координа́т — co-ordinate converterпреобразова́тель мод — mode changer, mode transducer, mode transformerпреобразова́тель напряже́ние — код — voltage-to-number converterпреобразова́тель по́лного сопротивле́ния — impedance transformerпьезоква́рцевый преобразова́тель — piesoelectric temperature transducerрту́тный преобразова́тель — mercury-arc converterпреобразова́тель систе́мы счисле́ния — radix converterпреобразова́тель стро́чного станда́рта тлв. — line-scan conversion unitпреобразова́тель телевизио́нных станда́ртов — television standard converterтермоэлектри́ческий преобразова́тель — thermoelectric temperature transducerпреобразова́тель то́ка, стати́ческий — static converterпреобразова́тель то́ка, тири́сторный — thyristor converterпреобразова́тель то́ка, электромаши́нный одноя́корный — rotary converterпреобразова́тель углово́го перемеще́ния в код — shaft position-to-digital converter, shaft digitizerпреобразова́тель у́гол — код — shaft (angle) encoderфункциона́льный преобразова́тель — function generatorфункциона́льный, дио́дный преобразова́тель — diode function generatorфункциона́льный преобразова́тель на ЭЛТ — cathode-ray tube function generatorфункциона́льный преобразова́тель на ЭЛТ за́мкнутого ти́па — photoformerци́фро-ана́логовый преобразова́тель — digital-to-analog [D/ A] converterпреобразова́тель частоты́ — frequency converterпреобразова́тель частоты́, ве́нтильный [ПЧВ] — valve-type frequency corverterпреобразова́тель частоты́, колле́кторный — commutator-type frequency converterпреобразова́тель частоты́, параметри́ческий — parametric frequency converterпреобразова́тель частоты́, стати́ческий [ПС] — static frequency converterпреобразова́тель частоты́, тиратро́нный — thyratron frequency changerпреобразова́тель частоты́, электромаши́нный — rotary frequency changerэлектроакусти́ческий преобразова́тель — acoustical-electrical transducerэлектро́нно-опти́ческий преобразова́тель — electrooptical transducer, image converter tubeпреобразова́тель эне́ргии — energy converterпреобразова́тель эне́ргии, термомагни́тный — thermomagnetic energy converterпреобразова́тель эне́ргии, термоэмиссио́нный — thermionic energy converterпреобразова́тель эне́ргии, электромехани́ческий — electromechanical energy converter -
14 Tesla, Nikola
SUBJECT AREA: Electricity[br]b. 9 July 1856 Smiljan, Croatiad. 7 January 1943 New York, USA[br]Serbian (naturalized American) engineer and inventor of polyphase electrical power systems.[br]While at the technical institute in Graz, Austria, Tesla's attention was drawn to the desirability of constructing a motor without a commutator. He considered the sparking between the commutator and brushes of the Gramme machine when run as a motor a serious defect. In 1881 he went to Budapest to work on the telegraph system and while there conceived the principle of the rotating magnetic field, upon which all polyphase induction motors are based. In 1882 Tesla moved to Paris and joined the Continental Edison Company. After building a prototype of his motor he emigrated to the United States in 1884, becoming an American citizen in 1889. He left Edison and founded an independent concern, the Tesla Electric Company, to develop his inventions.The importance of Tesla's first patents, granted in 1888 for alternating-current machines, cannot be over-emphasized. They covered a complete polyphase system including an alternator and induction motor. Other patents included the polyphase transformer, synchronous motor and the star connection of three-phase machines. These were to become the basis of the whole of the modern electric power industry. The Westinghouse company purchased the patents and marketed Tesla motors, obtaining in 1893 the contract for the Niagara Falls two-phase alternators driven by 5,000 hp (3,700 kW) water turbines.After a short period with Westinghouse, Tesla resigned to continue his research into high-frequency and high-voltage phenomena using the Tesla coil, an air-cored transformer. He lectured in America and Europe on his high-frequency devices, enjoying a considerable international reputation. The name "tesla" has been given to the SI unit of magnetic-flux density. The induction motor became one of the greatest advances in the industrial application of electricity. A claim for priority of invention of the induction motor was made by protagonists of Galileo Ferraris (1847–1897), whose discovery of rotating magnetic fields produced by alternating currents was made independently of Tesla's. Ferraris demonstrated the phenomenon but neglected its exploitation to produce a practical motor. Tesla himself failed to reap more than a small return on his work and later became more interested in scientific achievement than commercial success, with his patents being infringed on a wide scale.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsAmerican Institute of Electrical Engineers Edison Medal 1917. Tesla received doctorates from fourteen universities.Bibliography1 May 1888, American patent no. 381,968 (initial patent for the three-phase induction motor).1956, Nikola Tesla, 1856–1943, Lectures, Patents, Articles, ed. L.I.Anderson, Belgrade (selected works, in English).1977, My Inventions, repub. Zagreb (autobiography).Further ReadingM.Cheney, 1981, Tesla: Man Out of Time, New Jersey (a full biography). C.Mackechnie Jarvis, 1969, in IEE Electronics and Power 15:436–40 (a brief treatment).T.C.Martin, 1894, The Inventions, Researches and Writings of Nikola Tesla, New York (covers his early work on polyphase systems).GW -
15 Thomson, Elihu
SUBJECT AREA: Electricity[br]b. 29 March 1853 Manchester, Englandd. 13 March 1937 Swampscott, Massachusetts, USA[br]English (naturalized) American electrical engineer and inventor.[br]Thomson accompanied his parents to Philadelphia in 1858; he received his education at the Central High School there, and afterwards remained as a teacher of chemistry. At this time he constructed several dynamos after studying their design, and was invited by the Franklin Institute to give lectures on the subject. After observing an arc-lighting system operating commercially in Paris in 1878, he collaborated with Edwin J. Houston, a senior colleague at the Central High School, in working out the details of such a system. An automatic regulating device was designed which, by altering the position of the brushes on the dynamo commutator, maintained a constant current irrespective of the number of lamps in use. To overcome the problem of commutation at the high voltages necessary to operate up to forty arc lamps in a series circuit, Thomson contrived a centrifugal blower which suppressed sparking. The resulting system was efficient and reliable with low operating costs. Thomson's invention of the motor meter in 1882 was the first of many such instruments for the measurement of electrical energy. In 1886 he invented electric resistance welding using low-voltage alternating current derived from a transformer of his own design. Thomson's work is recorded in his technical papers and in the 700plus patents granted for his inventions.The American Electric Company, founded to exploit the Thomson patents, later became the Thomson-Houston Company, which was destined to be a leader in the electrical manufacturing industry. They entered the field of electric power in 1887, supplying railway equipment and becoming a major innovator of electric railways. Thomson-Houston and Edison General Electric were consolidated to form General Electric in 1892. Thomson remained associated with this company throughout his career.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsChevalier and Officier de la Légion d'honneur 1889. American Academy of Arts and Sciences Rumford Medal 1901. American Institute of Electrical Engineers Edison Medal 1909. Royal Society Hughes Medal 1916. Institution of Electrical Engineers Kelvin Medal 1923, Faraday Medal 1927.Bibliography1934, "Some highlights of electrical history", Electrical Engineering 53:758–67 (autobiography).Further ReadingD.O.Woodbury, 1944, Beloved Scientist, New York (a full biography). H.C.Passer, 1953, The Electrical Manufacturers: 1875–1900, Cambridge, Mass, (describes Thomson's industrial contribution).K.T.Compton, 1940, Biographical Memoirs of Elihu Thomson, Washington, DCovides an abridged list of Thomson's papers and patents).GW -
16 гальваническая развязка
гальваническая развязка
Мероприятие или техническое средство, применение которого направлено на исключение гальванической связи между проводящими частями.
[РД-91.020.00-КТН-276-07]
гальваническая развязка
Схемотехническое решение, при котором исключается гальваническая связь между электрическими цепями. Гальваническая развязка осуществляется трансформаторами или оптоэлектронными приборами.
[Интент]EN
galvanic separation
prevention of electric conduction between two electric circuits intended to exchange power and/or signals
NOTE – Galvanic separation can be provided e.g. by an isolating transformer or an opto-coupler.
[IEV number 151-12-26]FR
séparation électrique, f
séparation galvanique (terme déconseillé), f
action ou moyen d’empêcher la conduction électrique entre deux circuits électriques prévus pour échanger de la puissance ou des signaux
NOTE – Une séparation électrique peut être obtenue, par exemple, au moyen d’un transformateur de séparation (de circuits) ou d’un optocoupleur.
[IEV number 151-12-26]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Electrical isolation means that no current flow can occur from one electric circuit to a neighboring other electric circuit.
In case of power supplies, this means that no electric connection exists between the input side and the output side.
[ABB]Гальваническая развязка означает, что электрический ток не может протекать из какой-либо цепи в соседнюю цепь.
Для источников электропитания это означает, что не существует электрической связи между входной и выходной сторонами.
[Перевод Интент]The measured values are electrically isolated.
[Schneider Electric]Измеряемые величины гальванически развязаны от цепей устройства.
[Перевод Интент]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Близкие понятия
EN
DE
- galvanische Trennung
- Wellenimpedanz, (Leitungs-)
FR
3.4.3 гальваническая развязка (galvanic isolation): Элемент в искробезопасном электрооборудовании, посредством которого обеспечивается передача сигнала со входа на выход без прямого электрического соединения между ними.
Примечание - Для гальванической развязки часто используют либо магнитные (трансформаторы или реле), либо оптронные элементы.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 52350.14-2006: Электрооборудование для взрывоопасных газовых сред. Часть 14. Электроустановки во взрывоопасных зонах (кроме подземных выработок) оригинал документа
3.5.3 гальваническая развязка (galvanic isolation): Элемент в искробезопасном или связанном электрооборудовании, посредством которого обеспечивают передачу сигналов или мощности между электрическими цепями без прямого электрического соединения между ними.
Примечание - Для гальванической развязки часто используют либо магнитные (трансформаторы или реле), либо оптронные элементы.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60079-14-2008: Взрывоопасные среды. Часть 14. Проектирование, выбор и монтаж электроустановок оригинал документа
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > гальваническая развязка
-
17 обмотка
обмотка
Совокупность витков, образующих электрическую цепь с целью получения одного из напряжений трансформатора.
Примечание — Для трехфазного трансформатора под «обмоткой» подразумевается совокупность соединяемых между собой обмоток одного напряжения всех фаз, см. 3.3.3
(МЭС 421-03-01).
[ ГОСТ 30830-2002]
обмотка
Ндп. намотка
По ГОСТ 18311-80
[ ГОСТ 20718-75]
обмотка
Изолированный проводник, уложенный в специфическом порядке, предназначенный для возбуждения магнитного поля при протекании по нему электрического тока
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]
обмотка
-
[IEV number 151-13-17]EN
winding
the assembly of turns forming an electric circuit associated with one of the voltages assigned to the transformer or to the reactor
NOTE – For a polyphase transformer or polyphase reactor, the "winding" is the combination of the phase windings
[IEV number 421-03-01]
winding
assembly of interconnected turns and/or coils intended for common operation
NOTE – A winding is provided with terminals and is intended to produce a magnetic field when carrying electric currents or to produce voltages between appropriate points when placed in a time-varying magnetic field or moved through a magnetic field.
[IEV number 151-13-17]FR
enroulement
ensemble des spires formant un circuit électrique associé à l'une des tensions pour lesquelles le transformateur ou la bobine d'inductance ont été établis
NOTE – Pour un transformateur polyphasé ou pour une bobine d'inductance polyphasée, l"enroulement" est l'ensemble des enroulements de phase.
[IEV number 421-03-01]
enroulement, m
ensemble de spires ou de bobines interconnectées et destinées à fonctionner conjointement
NOTE – Un enroulement est muni de bornes et est destiné à produire un champ magnétique lorsqu’il est parcouru par des courants électriques ou à produire des tensions électriques entre des points appropriés lorsqu’il est placé dans un champ magnétique variable dans le temps ou déplacé dans un champ magnétique.
[IEV number 151-13-17]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Классификация
>>>EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > обмотка
-
18 Jablochkoff, Paul
[br]b. 14 September 1847 Serdobsk, Russiad. April 1894 St Petersburg, Russia[br]Russian military engineer and inventor of an electric "candle", the invention of which gave an immense impetus to electric lighting in the 1870s.[br]Jablochkoff studied at the Military Engineering College in St Petersburg. Having a scientific bent, he was sent to the Military Galvano Technical School. At the end of his military service in 1871 he was appointed Director General of the Moscow-Kursk telegraph lines for the Midi Railway Company. At this time he began to develop an interest in electric lighting, and in 1875 he left the Imperial Telegraph Service to devote his time exclusively to scientific pursuits. He found employment at the workshop of M Bréguet in Paris, where Gramme dynamos and Serrin arc lamps were being constructed. After some experimentation he found a means of producing a carbon arc that regulated itself without any mechanism. This lamp, the Jablochkoff candle, with two carbon rods placed parallel to each other and so close that an arc formed at the ends, could continue to burn until the rods were consumed. Plaster of Paris was used to separate the two electrodes and crumbled away as the carbon burned, thus exposing fresh carbon. These lamps were used in May 1878 in Paris to illuminate the avenue de l'Opéra, and later in Rome and London, and in essence were the first practical electric street lighting. Since there was no regulating mechanism, several candles could be placed in a single circuit. Despite inherent defects, such as the inability to restart the lamps after they were extinguished by wind or interruption of supply, they remained in use for some purposes for several years on account of their simplicity and cheapness. In 1877 Jablochkoff obtained the earliest patent to employ transformers to distribute current in an alternating-current circuit.[br]Bibliography11 September 1876, British patent no. 3,552 (Jablochkoff's candle).22 May 1877, British patent no. 1,996 (transformer or induction coil distribution).Further ReadingW.J.King, 1962, The Development of Electrical Technology in the 19th Century, Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution, Paper 30, pp. 393–407 (a detailed account). W.E.Langdon, 1877, "On a new form of electric light", Journal of the Society ofTelegraph Engineers 6:303–19 (an early report on Jablochkoffs system).Engineering (1878) 26:125–7.GW -
19 электродвигатель
(электро) двигатель (электропривода)
Электромеханический преобразователь, предназначенный для преобразования электрической энергии в механическую.
Примечание. В некоторых режимах работы электропривода электродвигатель осуществляет обратное преобразование энергии.
[ ГОСТ Р 50369-92]
электродвигатель
-
[IEV number 151-13-41]EN
(electric) motor
electric machine intended to transform electric energy into mechanical energy
Source: 411-03-01 MOD
[IEV number 151-13-41]FR
moteur (électrique), m
machine électrique destinée à transformer de l'énergie électrique en énergie mécanique
Source: 411-03-01 MOD
[IEV number 151-13-41]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электродвигатель
-
20 электрооборудование
электрооборудование
Совокупность электротехнических изделий и (или) электротехнических устройств, предназначенных для выполнения заданной работы. Электрооборудование в зависимости от объекта установки имеет соответствующее наименование, например, электрооборудование автомобиля и др.
[Макаров Е.Ф. Справочник по электрическим сетям 0,4-35 кВ и 110-1150 кВ]
электрооборудование
Совокупность электротехнических устройств, объединенных общими признаками.
Примечание.
Признаками объединения в зависимости от задачи могут быть: назначение, например, технологическое; условия применения, например, тропическое; принадлежность к объекту, например, станку, цеху.
[ ГОСТ 18311-80]
электрооборудование
Любое оборудование, предназначенное для производства, преобразования, передачи, аккумулирования, распределения или потребления электрической энергии, например машины, трансформаторы, аппараты, измерительные приборы, устройства защиты, кабельная продукция, бытовые электроприборы
(МЭС 826-07-01).
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61140-2000]
электрическое оборудование
Оборудование, используемое для производства, преобразования, передачи, распределения или потребления электрической энергии.
Примечание - Примерами электрического оборудования могут быть электрические машины, трансформаторы, коммутационная аппаратура и аппаратура управления, измерительные приборы, защитные устройства, электропроводки, электроприемники
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
электрооборудование
Оборудование, предназначенное для производства, передачи и изменения характеристик электрической энергии, а также для её преобразования в другой вид энергии.
К электрооборудованию нормативные и правовые документы относят электродвигатели, трансформаторы, коммутационную аппаратуру, аппаратуру управления, защитные устройства, измерительные приборы, кабельные изделия, бытовые электрические приборы и другие электротехнические изделия. Электрооборудование используют для производства электрической энергии, изменения её характеристик (напряжения, частоты, вида электрического тока и др.), передачи, распределения электроэнергии и, в конечном итоге, – для её преобразования в другой вид энергии. Электрооборудование, применяемое в электроустановках зданий, обычно предназначено для преобразования электрической энергии в механическую, тепловую и световую энергию, то есть оно представляет собой электроприёмники.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%DD/view/96/]N
equipment
single apparatus or set of devices or apparatuses, or the set of main devices of an installation, or all devices necessary to perform a specific task
NOTE – Examples of equipment are a power transformer, the equipment of a substation, measuring equipment.
[IEV number 151-11-25]
electric equipment
item used for such purposes as generation, conversion, transmission, distribution or utilization of electric energy, such as electric machines, transformers, switchgear and controlgear, measuring instruments, protective devices, wiring systems, current-using equipment
[IEV number 826-16-01]FR
équipement, m
matériel, m
appareil unique ou ensemble de dispositifs ou appareils, ou ensemble des dispositifs principaux d'une installation, ou ensemble des dispositifs nécessaires à l'accomplissement d'une tâche particulière
NOTE – Des exemples d’équipement ou de matériel sont un transformateur de puissance, l’équipement d’une sous-station, un équipement de mesure.
[IEV number 151-11-25]
matériel électrique, m
matériel utilisé pour la production, la transformation, le transport, la distribution ou l'utilisation de l'énergie électrique, tel que machine, transformateur, appareillage, appareil de mesure, dispositif de protection, canalisation électrique, matériels d'utilisation
[IEV number 151-11-25]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Ausrüstung
- Betriebsmittel
- elektrisches Betriebsmittel, n
FR
- matériel
- matériel électrique, m
- équipement
2. Электрооборудование
Electrical equipment
Совокупность электротехнических устройств, объединенных общими признаками.
Примечание. Признаками объединения в зависимости от задачи могут быть: назначение, например, технологическое; условия применения, например, тропическое; принадлежность к объекту, например, станку, цеху
Источник: ГОСТ 18311-80: Изделия электротехнические. Термины и определения основных понятий оригинал документа
3.7 электрооборудование (electrical apparatus): Оборудование, в целом или по частям предназначенное для использования электрической энергии.
Примечание - Помимо остальных частей, это части для генерирования, передачи, распределения, хранения, измерения, регулирования, переработки и потребления электрической энергии и части для телекоммуникации.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 61241-0-2007: Электрооборудование, применяемое в зонах, опасных по воспламенению горючей пыли. Часть 0. Общие требования оригинал документа
3.10 электрооборудование (electrical apparatus): Оборудование, полностью или частично предназначенное для использования электрической энергии.
Примечание - К электрооборудованию также относятся части электрооборудования, предназначенные для генерирования, передачи, распределения, хранения, измерения, регулирования, переработки и потребления электрической энергии и для телекоммуникации.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 61241-14-2008: Электрооборудование, применяемое в зонах, опасных по воспламенению горючей пыли. Часть 14. Выбор и установка оригинал документа
3.10 электрооборудование (electrical apparatus): Оборудование, полностью или частично предназначенное для использования электрической энергии.
Примечание - К электрооборудованию также относятся части электрооборудования, предназначенные для генерирования, передачи, распределения, хранения, измерения, регулирования, переработки и потребления электрической энергии и для телекоммуникации.
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электрооборудование
См. также в других словарях:
electric transformer — Смотри электрический трансформатор … Энциклопедический словарь по металлургии
Electric power transmission — Electric transmission redirects here. For vehicle transmissions, see diesel electric transmission. 400 kV high tension transmission lines near Madrid Electric power transmission or high voltage electric transmission is the bulk transfer of… … Wikipedia
Transformer oil — is usually a highly refined mineral oil that is stable at high temperatures and has excellent electrical insulating properties. It is used in oil filled transformers, some types of high voltage capacitors, fluorescent lamp ballasts, and some… … Wikipedia
Electric heating — is any process in which electrical energy is converted to heat. Common applications include heating of buildings, cooking, and industrial processes. An electric heater is an electrical appliance that converts electrical energy into heat. The… … Wikipedia
Electric resistance welding — (ERW) refers to a group of welding processes such as spot and seam welding that produce coalescence of faying surfaces where heat to form the weld is generated by the electical reistance of material vs the time and the force used to hold the… … Wikipedia
transformer — UK US /trænsˈfɔːmər/ noun [C] ► a piece of electrical equipment that changes the force of an electrical current: »an electric/electrical/power transformer … Financial and business terms
Electric rotating machinery — includes:* Electric motor * Electrical generator * Motor generator * Rotary transformer … Wikipedia
Transformer — This article is about the electrical device. For the toy line franchise, see Transformers. For other uses, see Transformer (disambiguation). Pole mounted distribution transformer with center tapped secondary winding. This type of transformer is… … Wikipedia
Electric motor — For other kinds of motors, see motor (disambiguation). For a railroad electric engine, see electric locomotive. Various electric motors. A 9 volt PP3 transistor battery is in the center foreground for size comparison. An electric motor converts… … Wikipedia
Electric power distribution — … Wikipedia
Electric arc furnace — An electric arc furnace (EAF) is a furnace that heats charged material by means of an electric arc. Arc furnaces range in size from small units of approximately one ton capacity (used in foundries for producing cast iron products) up to about 400 … Wikipedia
